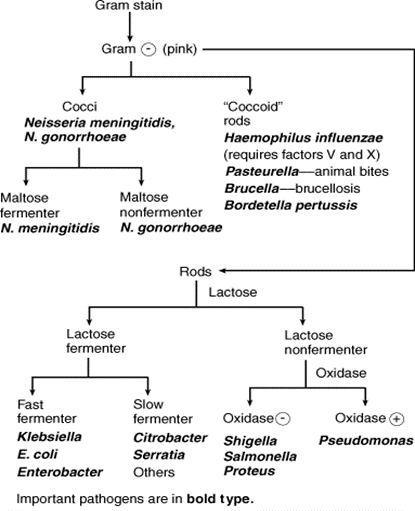
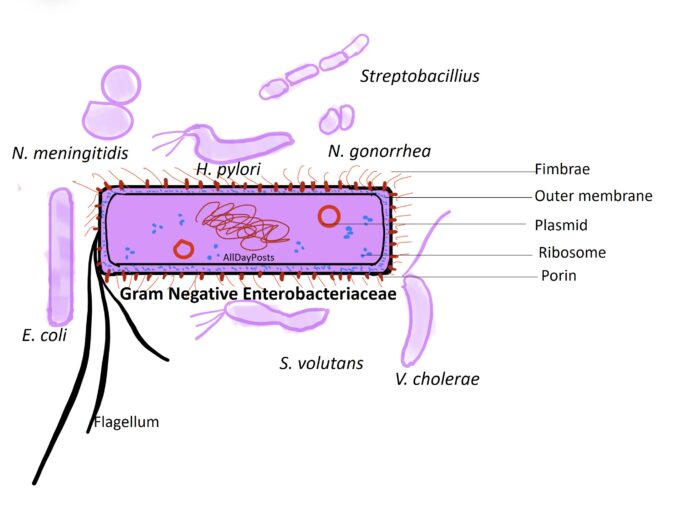
The Enterobacteriaceae is large family of Gram-negative bacteria. They are isolated in the medical setting and are responsible for several types of infections counting urinary tract infections, blood stream infections, food borne infections, and meningitis among others. The natural habitat of the bacteria is the intestinal tract of man and animals. The Enterobacteriaceae comprises rod-shaped bacteria that are metabolically active and can grow in artificial media. They can grow in either aerobic or anaerobic condition. Some species are motile can ferment wide range of carbohydrates. They also have a complex antigenic structure, and able to produce toxins and other virulence factors.
The Enterobacteriaceae family is composed of several defined groups of bacteria, such as, Shigella, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter etc. Each group is classified according to the similarity of biochemical reactions displayed by the organisms. For an instance Shigella and Escherichia are closely related to each other, both biochemically and serologically. The organisms with same phenotypic properties were categorized into same group or species. However, in recent days, the techniques like nucleic acid hybridization and nucleic acid sequencing are widely used to identify the bacteria species. They are also used to determine the relationship between different organisms. The Enterobacteriaceaeinclude more than 63 genera and 100 species. Nonetheless, 20-25 species are clinically important and others are encountered rarely.
(Source: Gomella LG, Haist SA; Clinician’s Pocket Reference, Eleventh Edition: http://www.accessmedicine.com)