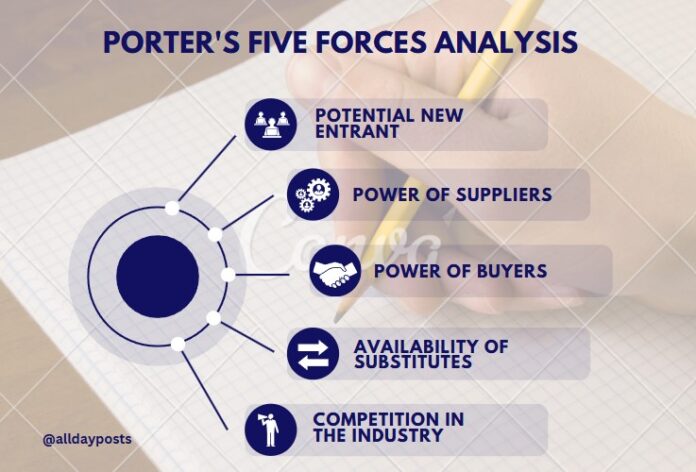
The Porter’s Five Forces model is an analysis tool to identify where power lies in a certain business situation by using the outside-in perspective. This is used to recognize industry structure to determine company strategy and action plan. It is essential to understand the level of competition within the industry so that company survives in market with long term profitability.
The competitive rivalry analyzes how intense the competition is in market. It considers number of existing competitors and their capability in marketplace. When rivalry competition is high there will be an impact on business bottom line. This either because of price war or massive investment in sales & marketing for product promotion. The supplier power analyzes how much power a supplier has and how easy for them to drive up prices. It is obvious that fewer the suppliers, the more power they have. Therefore, business will be in better position if there are multiple suppliers. The buyer power of customer examines how easy it is for the buyer to drive down price and their effect on product pricing and quality. If there are plenty of seller, it will be easy for customer to switch. In addition, bargain power of customer is low when they purchase the product in small volume. The threat of new entrant examines how easy of difficult is for competitor to join the marketplace. The market share will be decreased if there is easier for competitor to enter the market. The threat of substitution will examine how easy it is for customer to switch from a one product to the competitor product. The number of competitors, their pricing strategy, product quality, marketing activity etc. are crucial. Most importantly, it also studies the competitors profit even if they lower the price.
Reference: Johnson, G., Scholes, K., & Whittington, R. (2008). Exploring corporate strategy: text and cases. Pearson Education.